What is Epigenetics?
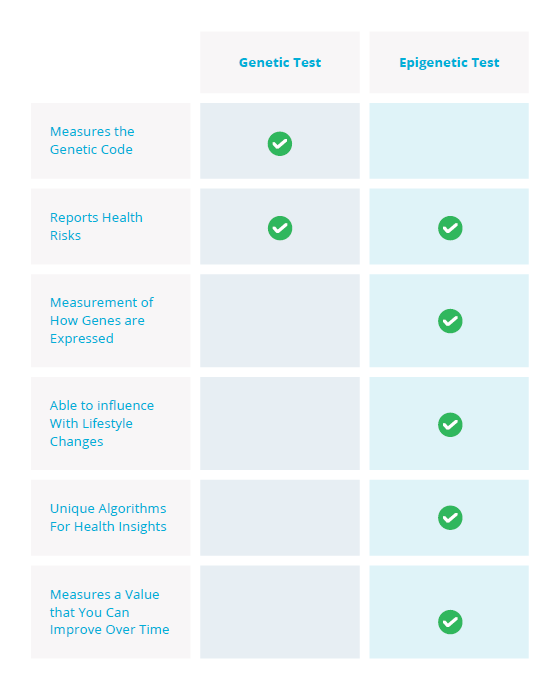
Epigenetics is the study of how genes are expressed, without any effect on the underlying DNA sequence. The prefix “epi-” means “on top of” or “beyond”. As such, epigenetics looks at factors that influence gene expression that are not encoded in the DNA sequence itself. Imagine your DNA as a musical score, and epigenetics as the conductor, determining which instruments play and how loudly. Epigenetic modifications are changes to the DNA that regulate whether the genes are turned on or off. These changes can arise from a diverse range of factors, such as environmental influences, lifestyle habits and dietary choices, among others.
One of the most common types of epigenetic modification is DNA methylation. This process involves adding a hydrocarbon group (methyl) to specific regions in the DNA, typically between cytosine and guanine nucleotides. This methylation acts as a molecular flag, attracting proteins that repress gene expression. On the other hand, the absence of methylation can signal for genes to be actively transcribed and translated to proteins. DNA methylation patterns can give you valuable insights into your aging process and various health conditions including risks with cancer, neurological diseases, autoimmune diseases and chronic diseases.
Our epigenetic test, MyTruHealth, examines the positioning and quantity of methyl groups on your DNA, providing valuable insights on alterations affecting your gene expression and their tangible impact on the body, rather than solely focusing on the DNA sequence. These tests empowers you with comprehensive information pertaining to your health status and the potential risk of developing certain diseases. As our understanding of epigenetics grows, epigenetic tests are likely to become even more important in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of disease.

Discover Your Biological Age

Chronological Age

Biological Age
Discover Your Biological Age

Chronological Age is the number of years that have passed since your birth. It has little to do with how you feel and how your body functions. It cannot be influenced by lifestyle and habits.
Biological Age is how old your cells are and how well your body is functioning. It can be reversed by attending to your health.

When your body ages more rapidly than the passage of calendar years, you are undergoing accelerated biological aging. Biological age has emerged as a significant indicator of risk for chronic diseases, neurological functions, as well as mortality and morbidity rates. Fortunately, there are lifestyle and medical interventions that have been proven effective in slowing down, halting, or even reversing the biological aging processes within your body. By measuring your baseline and monitoring changes in your rate of aging, you gain the ability to guide your journey towards anti-aging, health, and overall well-being in the desired direction.
Age Healthier to Live Better
Factors Affecting Biological Age
Start your anti-aging journey by knowing various epigenetics read outs relating to aging.

Based on the Bioage and Pace of Aging results, implement lifestyle interventions.
Retest your pace of aging (the most change-sensitive measurement) to gauge your hard work and intervention effectiveness.
The concept of Biological Age is crucial for establishing the connection between epigenetics and health.
Mounting evidence suggests that Biological Age is a more reliable indicator of overall health and disease vulnerability than chronological age. Consequently, it is crucial to acknowledge the profound influence of aging as the primary risk factor for a range of chronic illnesses. Biological Age measurement captures the alterations in DNA methylation patterns and converts them into a numerical value. This approach enables a straightforward yet comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s overall health.
Ideally, everyone would want their biological age to be younger than their chronological age. This means that they are living a healthy lifestyle that will help them stay healthy and prevent sickness and disease for a longer period of time. Great news awaits! The realm of epigenetics brings hope as it unveils the reversibility of epigenetic changes, including DNA methylation. Yes, you read it right – epigenetic aging is reversible. Now, armed with a direct measure of aging, we hold the key to slowing down the relentless march of biological aging!












